E) Reviewing User Access Privileges Under Glba Law
ISO 27001 – Annex A.9: Access Control
Your pace-by-step guide to understanding and coming together Annex A.9 of ISO 27001
Get your free guide to achieving ISO 27001
×
Your ultimate guide to beginning-time ISO 27001 success

Nosotros merely need a few details so that we can send you your guide to achieving ISO 27001 beginning-time
Download your free guide now and if you have any questions at all then Book a Demo or Contact Us. Nosotros'll be happy to help.

Understanding Annex A.9
Addendum A.9 is all virtually access control procedures. The aim of Annex A.9 is to safeguard access to data and ensure that employees can only view data that'south relevant to their work.
This is a key part to become correct in your journey to ISO 27001 certification and one where a lot of companies find they need support. If yous're looking for a simplified way to get certified and so we propose taking a look at our ISMS.online platform which will give y'all a 77% head start.
Annex A.9 is divided into four sections and y'all will need to work through each one. They are Access Controls, User Access Direction, User Responsibilities and Application Admission Controls.
What is the objective of Annex A.nine.ane of ISO 27001?
Annex A.nine.1 is nigh business organization requirements of access command. The objective in this Annex A command is to limit admission to information and information processing facilities.
It'due south an of import part of the data security direction system (ISMS) especially if you'd like to achieve ISO 27001 certification. Lets sympathize those requirements and what they mean in a bit more depth.
A.9.ane.i Admission Control Policy
An access control policy must be established, documented and reviewed regularly taking into account the requirements of the business for the assets in scope.
Access control rules, rights and restrictions along with the depth of the controls used should reverberate the data security risks around the information and the system'due south appetite for managing them. Put simply admission control is about who needs to know, who needs to use and how much they get access to.
Access controls tin be digital and physical in nature, e.g. permission restrictions on user accounts as well as limitations on who tin access certain concrete locations (aligned with Annex A.11 Concrete and Environs Security). The policy should take into account:
- Security requirements of business applications and align with the data classification scheme in use as per A.8 Asset Management;
- Clarify who needs to admission, know, who needs to use the data – supported past documented procedures and responsibilities;
- Management of the admission rights and privileged access rights (more power – see beneath) including adding, in life changes (e.1000. super users/administrators controls) and periodic reviews (east.g. by regular internal audits in line with requirement 9.2.
- Admission control rules should be supported past formal procedures and defined responsibilities;
Access control needs to be reviewed based on change in roles and in detail during exit, to marshal with Addendum A.7 Human Resource Security.
A.ix.ane.ii Access to Networks and Network Services
The principle of least access is the general arroyo favoured for protection, rather than unlimited access and superuser rights without careful consideration.
Equally such users should only go access to the network and network services they need to use or know nigh for their job. The policy therefore needs to accost; The networks and network services in scope for access; Say-so procedures for showing who (role based) is allowed to admission to what and when; and Management controls and procedures to prevent access and monitor it in life.
This also needs to be considered during onboarding and offboarding, and is closely related to the access command policy itself.

Achieve your first ISO 27001
Download your gratis guide to fast and sustainable certification
×
Your ultimate guide to first-time ISO 27001 success

We just need a few details and so that we can ship you your guide to achieving ISO 27001 kickoff-time
Download your free guide now and if you accept whatsoever questions at all then Book a Demo or Contact The states. We'll be happy to help.
Achieve your kickoff ISO 27001
Download our free guide to fast and sustainable certification
×
Your ultimate guide to starting time-time ISO 27001 success

Nosotros but need a few details so that we tin can send you your guide to achieving ISO 27001 get-go-time
Download your gratis guide now and if you have any questions at all and then Book a Demo or Contact Us. We'll be happy to help.
What is the objective of Addendum A.9.2 of ISO 27001?
Addendum A.9.2 is most user access direction. The objective in this Annex A control is to ensure users are authorised to access systems and services as well as prevent unauthorised admission.
A.9.2.1 User Registration and Deregistration
A formal user registration and deregistration process needs to be implemented. A good process for user ID management includes being able to acquaintance individual IDs to existent people, and limit shared access IDs, which should be approved and recorded where done.
A good on-boarding and leave process ties in with A7 Human Resource Security to evidence quick and clear registration/deregistration along with avoidance of reissuing old IDs. A regular review of ID'due south will illustrate practiced control and reinforces ongoing direction.
That can be tied in with the internal audits noted above for admission control audits, and periodic reviews by the information asset or processing awarding owners.
A.nine.2.ii User Admission Provisioning
A process (yet simple and documented) must be implemented to assign or revoke access rights for all user types to all systems and services. Washed well information technology ties in with the points above likewise as the broader Hr Security work.
Provisioning and revoking procedure should include; Authorisation from the owner of the information arrangement or service for the use of the information organization or service; Verifying that the access granted is relevant to the role being done; and protecting confronting provisioning being washed before authorisation is complete.
User access should ever exist business organisation led and access based around the requirements of the business. This might sound bureaucratic but it doesn't demand to be and constructive simple procedures with role based access by systems and services can address it.

Detect our platform
Book a tailored hands-on session
based on your needs and goals
Book your demo
Nosotros can't think of any company whose service can hold a candle to ISMS.online.
ISO 27001, 27701 and GDPR lead implementer Aperian Global
100% of our users pass certification first time
Book your demo
A.9.2.3 Management of Privileged Access Rights
A.nine.2.3 is about managing unremarkably more than powerful and higher 'privileged' levels of admission e.g. systems assistants permissions versus normal user rights.
The resource allotment and utilize of privileged access rights has to be tightly controlled given the extra rights usually conveyed over information assets and the systems controlling them. For case the power to delete work or fundamentally touch on the integrity of the information. It should align with the formal authorisation processes alongside the admission control policy.
That could include; system past system clarity on privileged access rights (which can be managed inside the awarding); allocation on a need-to-use ground not a blanket arroyo; A process and record of all privileges allocated should be maintained (aslope the information asset inventory or as office of the A.9 bear witness; and the competence of users granted the rights must be reviewed regularly to marshal with their duties.
This is another good expanse to include in the internal audit to demonstrate control.
I of the biggest contributory factors to failures or breaches of systems is inappropriate and blanket use of organisation administration privileges with homo mistake leading to more impairment or loss than if a 'least access' approach were taken.
Other good practice relating to this surface area includes the separation of the systems administrator role from the 24-hour interval to day user role and having a user with two accounts if they perform different jobs on the same platform.
See ISMS.online in action
- Uncomplicated and easy to employ
- Comprehensive in scope
- Affordable and lower toll than alternatives
Volume your demo
A.nine.2.4 Management of Surreptitious Authentication Data of Users
Hole-and-corner hallmark data is a gateway to admission valuable assets. It typically includes passwords, encryption keys etc. and then needs to exist controlled through a formal management process and needs to be kept confidential to the user.
This is usually tied into employment contracts and disciplinary processes (A.vii) and supplier obligations (A13.2.4 and A.15) if sharing with external parties.
Procedures should be established to verify the identity of a user prior to providing new, replacement or temporary undercover authentication information. Any default underground hallmark data provided as part of a new system use should be changed as shortly equally possible.
A.ix.2.5 Review of User Access Rights
Asset owners must review users' admission rights at regular intervals, both around individual change (on-boarding, change of part and exit) also broader audits of the systems admission.
Authorisations for privileged access rights should exist reviewed at more than frequent intervals given their college risk nature. This ties in with 9.2 for internal audits and should be done at least annually or when major changes take place.
A.nine.2.6 Removal or Adjustment of Access Rights
Every bit outlined above admission rights of all employees and external political party users to information and data processing facilities demand to be removed upon termination of their employment, contract or understanding, (or adjusted upon modify of role if required).
A good exit policy and procedures dovetailed in with A.vii will also ensure this is achieved and demonstrated for audit purposes when people exit.
With ISMS.online, challenges around version control, policy approval & policy sharing are a thing of the past.
Information technology Director NHS Professionals
100% of our users pass certification showtime time
Notice our platform
What is the objective of Annex A.ix.3 of ISO 27001?
Annex A.9.three is most user responsibilities. The objective in this Annex A control is to brand users answerable for safeguarding their authentication data.
A.9.three.ane Apply of Undercover Authentication Information
This is only about making sure that users follow the policies and will therefore tie in with A7 Human Resource Security for contracts, user education for awareness and compliance, besides as common sense practices.
These include: Keep any hole-and-corner hallmark information confidential; Avoid keeping a record of it that can be accessed by unauthorised parties; Alter information technology whenever there is any suggestion of possible compromise; select quality passwords with sufficient minimum length and force to follow broader password policy controls in Addendum A.9.four.
What is the objective of Annex A.nine.4 of ISO 27001?
Annex A.9.4 is near system and application access command. The objective in this Annex A control is to forbid unauthorised access to systems and applications.
A.9.4.1 Data Access Restriction
Access to information and awarding system functions must be tied into the admission control policy. Key considerations should include:
These include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC);
- Levels of admission;
- Design of "menu" systems inside applications;
- Read, write, delete and execute permissions;
- Limiting output of information; and
- Concrete and/or logical admission controls to sensitive applications, data and systems.
The auditor volition check to see that considerations accept been fabricated for limiting access within systems and applications that back up access control policies, business organization requirements, hazard levels and segregation of duties.
A.9.4.2 Secure log-on Procedures
Access to systems and applications must exist controlled by a secure log-on procedure to prove the identity of the user.
This can go beyond the typical password approach into multi-factor hallmark, biometrics, smart cards, and other means of encryption based on the risk being considered.
Secure log on should be designed and so it cannot be easily circumvented and that whatsoever hallmark information is transmitted and stored encrypted to foreclose interception and misuse.
ISO 27002 guidance is pregnant around this topic, as are specialist bodies similar the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC). Additional tips include:
- Log-on procedures should be designed and then that they cannot be easily circumvented and that any authentication information is transmitted and stored encrypted to prevent interception and misuse.
- Log-on procedures should also include a display stating that access is for authorised users only. This is designed to support cybersecurity legislation such as the Computer Misuse Act 1990 (Uk).
- Both a successful and unsuccessful log-on and log-off should be logged in a secure manner to provide forensic evidential power and alerts for unsuccessful attempts and possible lock-outs should be considered.
- Depending on the nature of the system access should be restricted to certain times of day or periods of time and potentially even be restricted according to location.
In practice, the business concern needs and information at risk should drive the log on and log off procedures. Information technology is not worth having 25 steps to log on, then have rapid time outs etc if staff are then unable to exercise their job well and spend a disproportionate amount of time in this loop.
A.9.four.3 Password Management Organization
The purpose of a password management system is to ensure quality passwords meet the required level and are consistently applied.
Password generation and management systems provide a good style of centralising the provisioning of access and they serve to reduce the risk of people using the same login for everything, equally illustrated in this little story of what happens when a customer contacts our team nigh a forgotten password!
As with any control machinery, password generation and management systems need to exist advisedly implemented to ensure adequate and proportionate levels of protection.
Wherever possible users should be able to cull their own passwords every bit this makes them easier to remember than machine-generated ones, notwithstanding, it needs to be upwards to a sure level of strength.
At that place are lots of conflicting views on password direction systems and password policies so nosotros encourage organisations to expect at the oftentimes changing best practices and adopt approaches based on the take a chance appetite and culture of the organisation.
As mentioned above, NCSC is a proficient place to review the latest practices or simply ask u.s.a. to introduce you lot to ane of our partners for help.
A.9.4.4 Utilize of Privileged Utility Programmes
Utility estimator programmes that might be capable of overriding system and awarding controls need to be carefully managed.
Powerful system and network utility programs tin can create an attractive target for malicious attackers and access to them must be restricted to the smallest number of people. As such utility programmes can be easily located and downloaded from the net it is also of import that users are restricted in their ability to install any software as much as possible weighed against business requirements and take a chance assessment. Utilise of utility programmes should exist logged and monitored/reviewed periodically to satisfy auditor requests.
A.9.iv.v Admission Command to Program Source Code
Admission to programme source lawmaking must exist restricted. Access to plan source code and associated items (such equally designs, specifications, verification plans and validation plans) should exist strictly controlled.
Programme source lawmaking can be vulnerable to assail if not fairly protected and tin provide an attacker with a skilful means to compromise systems in an frequently covert style. If the source code is central to the concern success it'south loss can also destroy the business value apace likewise.
Controls should include consideration for:
- Equally few people as possible having access
- Keeping source code off operational systems (just compiled code)
- Access to source code being as restricted as possible (deny-by-default)
- Access to source code existence logged and the logs periodically reviewed
- Strong and strict alter control procedures
- Frequent audits and reviews
Why is Addendum A.nine important?
Annex A.9 is probably the nearly talked about clause in the whole of Annex A, and some would argue it's the well-nigh important.
This is because your whole Data Security Management System (ISMS) is based on making certain the right people have access to the right information at the correct time. Getting that right is one of the keys to success, but getting it wrong tin can have a huge touch on your business organization.
Imagine if you lot accidentally gave access to confidential employee information to the wrong people, like revealing what anybody in the concern gets paid for example.
The consequences of getting this office wrong can exist significant, so information technology'south worth spending sufficient time thinking it all through.
This is where our platform can really help. It follows the whole structure of ISO 27001 and allows y'all to adopt, adapt and add to the content we provide giving you a big head start. To find out more why non book a demo?

Attain your first ISO 27001
Download your free guide to fast and sustainable certification
×
Your ultimate guide to kickoff-time ISO 27001 success

We only need a few details so that we can send you your guide to achieving ISO 27001 first-time
Download your free guide now and if you have any questions at all and then Book a Demo or Contact The states. We'll be happy to help.
We make achieving ISO 27001 easy
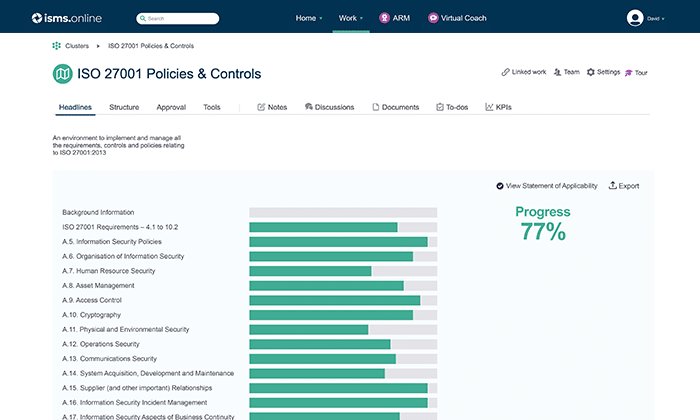
Get a 77% headstart
Our ISMS comes pre-configured with tools, frameworks and documentation y'all tin Adopt, Adjust or Add to. Elementary.
Learn more
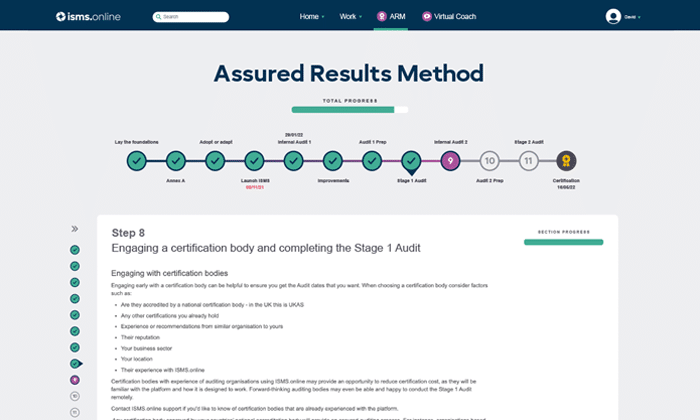
Your path to success
Our Bodacious Results Method is designed to become you certified on your outset endeavour. 100% success rate.
Learn more
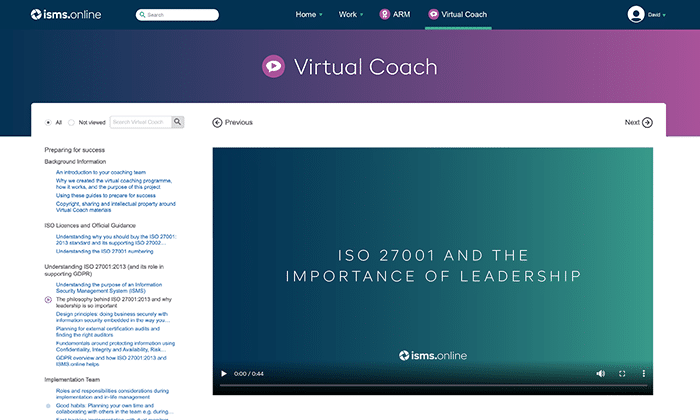
Lookout man and learn
Forget well-nigh time consuming and costly training. Our Virtual Motorbus video series is available 24/7 to guide you through.
Learn more
Platform features
Nosotros've developed a series of intuitive features and toolsets within our platform to salve you time and ensure y'all're building an ISMS that's truly sustainable. With ISMS.online you can quickly attain ISO 27001 certification and then maintain information technology with ease.

Policies & Controls Management
Hands interact, create and show you are on top of your documentation at all times
Find out more than

Simple Risk Management
Effortlessly address threats & opportunities and dynamically study on functioning
Observe out more than

Measurement & Automated Reporting
Make better decisions and show you lot are in command with dashboards, KPIs and related reporting
Notice out more than

Audits, Actions & Reviews
Make light piece of work of corrective actions, improvements, audits and direction reviews
Notice out more

Mapping & Linking Work
Shine a light on disquisitional relationships and elegantly link areas such equally assets, risks, controls and suppliers
Find out more

Interested Party Management
Visually map and manage interested parties to ensure their needs are clearly addressed
Observe out more

Documented Procedures
Simply document, easily command and publish your procedures to ensure stakeholders follow them
Find out more

Other Standards & Regulations
Neatly add in other areas of compliance affecting your arrangement to achieve even more
Find out more

Staff Compliance Assurance
Appoint staff, suppliers and others with dynamic end-to-cease compliance at all times
Find out more

Supply Chain Direction
Manage due diligence, contracts, contacts and relationships over their lifecycle
Discover out more than

User Management & Permissions
Practical permissions with depression cost plans for more regular and occasional users
Notice out more

Strong Privacy & Security
Strong privacy past blueprint and security controls to match your needs & expectations
Find out more than
joplinanswerpose80.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.isms.online/iso-27001/annex-a-9-access-control/
0 Response to "E) Reviewing User Access Privileges Under Glba Law"
Post a Comment